
What is Nato and which countries are members?
Nato, a military organisation for Western nations, is allowing more countries to join.
It is also increasing its defences, following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
What is Nato and when was it set up?
Nato – the North Atlantic Treaty Organization – was formed in 1949 by 12 countries, including the US, UK, Canada and France.
Its aim was to block expansion by the Soviet Union – a group of states which included Russia.
Members agree that if one of them is attacked, all other nations should help it – which could include using armed force.
Nato does not have an army of its own, but member countries can take joint military action in response to crises. They also coordinate military plans and carry out military exercises.
After its invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, Nato said that Russia was the “most significant and direct threat to allies’ security”.
Which countries are Nato members?
Nato has 31 members across Europe and North America.
After the Soviet Union’s collapse in 1991, many Eastern European countries joined: Albania, Bulgaria, Hungary, Poland, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Romania, Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia.
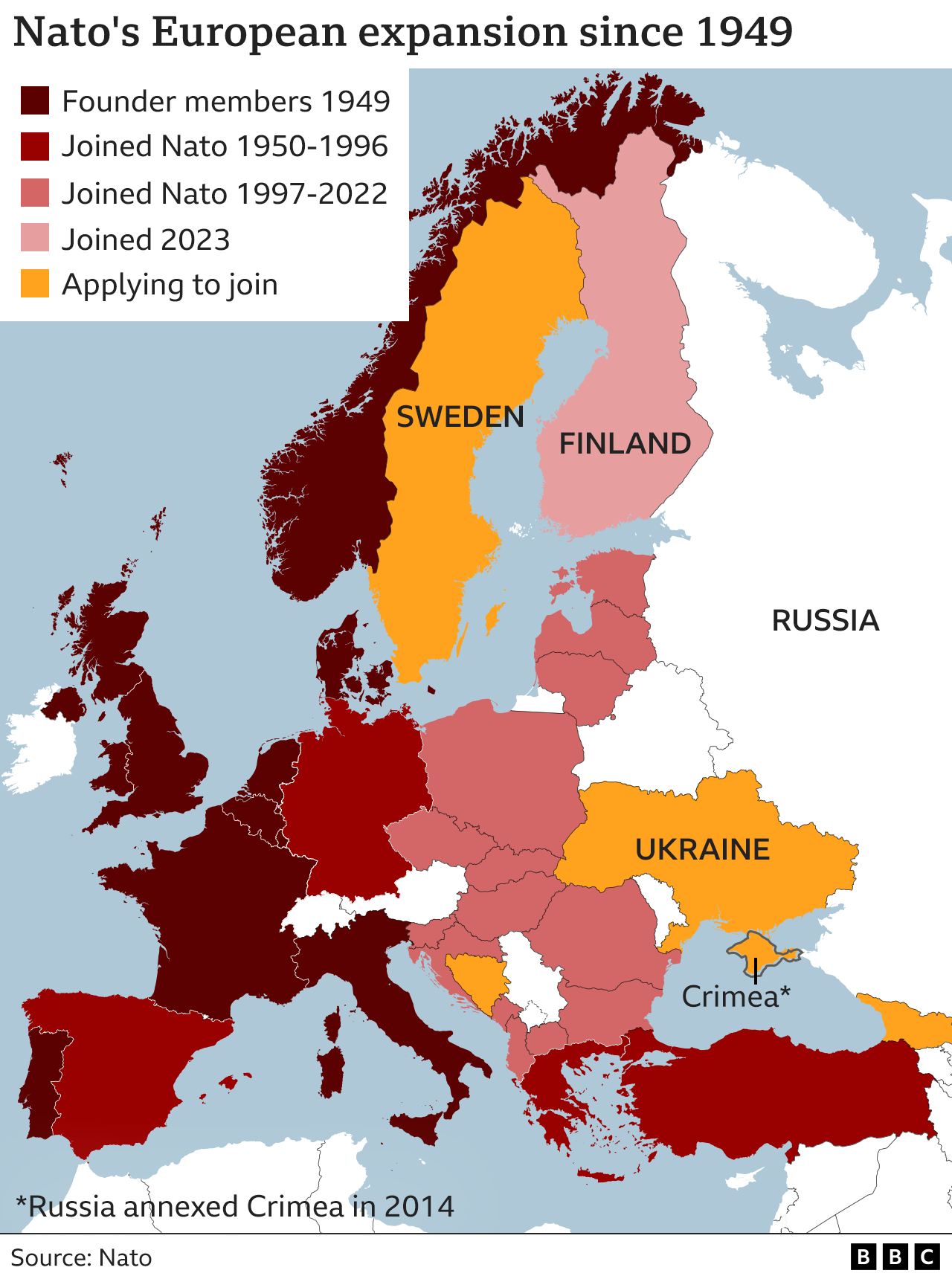
Sweden and Finland applied to join after Russia invaded Ukraine, because they feared for their security.
Finland – which has a 1,340km (832 mile) land border with Russia – became a member in April 2022.
Sweden’s membership has not yet been formally approved by two Nato members, Turkey and Hungary.
Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Georgia also want to join.
When will Ukraine join Nato?
Nato has said that Ukraine can become a member, but has not confirmed when this will happen.
It refused “fast-track” membership in September 2022.
Russia has opposed the idea of Ukraine joining Nato, fearing it would bring the alliance’s forces too close to its own territory.
Kyiv accepts it cannot join Nato while it is at war with Russia, but wants to join as soon as possible after fighting ends.
Since July 2023, the Nato-Ukraine Council has coordinated efforts to help Ukraine defend itself against Russia.
What weapons are Nato countries giving Ukraine?
As a group, Nato has not sent weapons to Ukraine, but several member countries have done so.
The US, UK, Germany and Turkey have provided anti-tank weapons, missile defence systems, artillery guns, tanks and military drones.
The US and UK have also supplied long-range missiles.

The US has let Nato countries offer its fighter jets, such as F-16s, to Ukraine, and teach pilots how to fly them.
The Netherlands has said it may soon deliver 18 F-16s.
However, Nato countries are not sending troops to Ukraine, or using their air forces to impose a no-fly zone, because that could provoke a direct conflict with Russia.
Since December, US politicians have failed to agree new funding for military aid for Ukraine. However, the UK government has pledged £2.5bn.
How is Nato increasing its defences against Russia?
In 2023, Nato commanders agreed detailed plans for countering possible Russian attacks in the Arctic and north Atlantic, in central Europe, or in the Mediterranean region.
In February 2024, Nato will stage one of its largest military exercises since the end of the Cold War.
The Steadfast Defender exercise in Eastern Europe will involve 90,000 personnel from all 31 Nato countries and Sweden. The UK is sending 20,000 personnel.
Nato previously announced plans to increase the number of its troops in Europe on high alert from 40,000 to more than 300,000.
It has also bolstered its defences on its eastern flank, bordering Russia.
It has eight battlegroups in Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania, Slovakia and the Baltic Republics. Before the war in Ukraine, it had four.
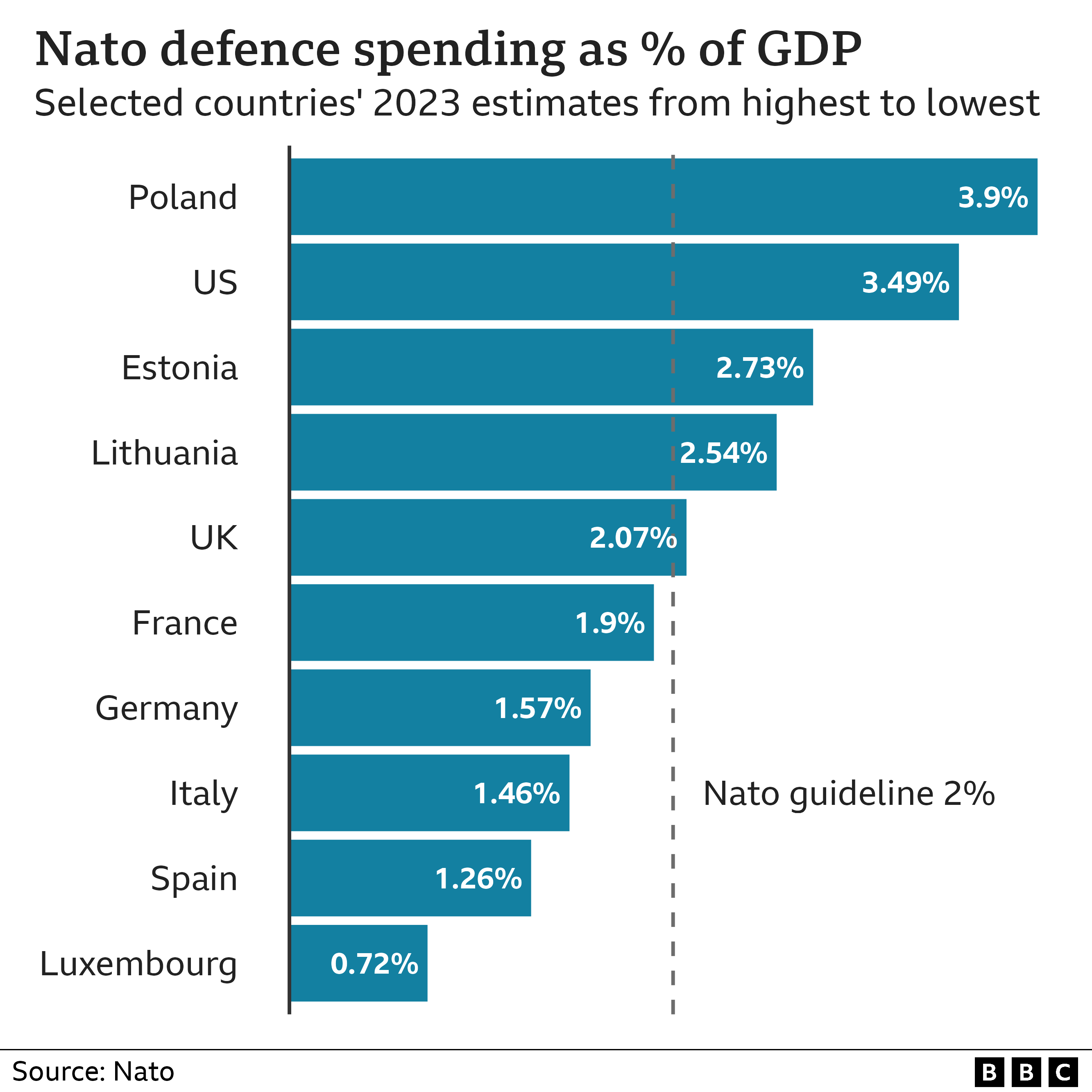
Nato countries have also been increasing their military budgets.
More are now spending more than 2% of their national incomes on defence – which Nato says is a minimum. However, many countries are spending less.
Comments (0)